94.binary-tree-inorder-traversal
Statement
Metadata
- Link: 二叉树的中序遍历
- Difficulty: Easy
- Tag:
栈树深度优先搜索二叉树
给定一个二叉树的根节点 root ,返回它的 中序 遍历。
示例 1:
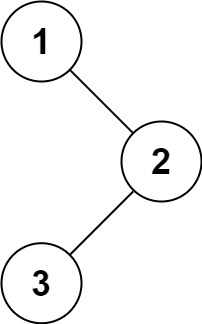
输入:root = [1,null,2,3]
输出:[1,3,2]
示例 2:
输入:root = []
输出:[]
示例 3:
输入:root = [1]
输出:[1]
示例 4:
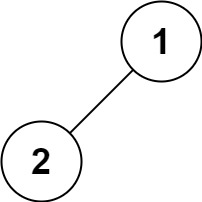
输入:root = [1,2]
输出:[2,1]
示例 5:
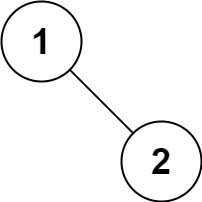
输入:root = [1,null,2]
输出:[1,2]
提示:
- 树中节点数目在范围
[0, 100]内 -100 <= Node.val <= 100
进阶: 递归算法很简单,你可以通过迭代算法完成吗?
Metadata
- Link: Binary Tree Inorder Traversal
- Difficulty: Easy
- Tag:
StackTreeDepth-First SearchBinary Tree
Given the root of a binary tree, return the inorder traversal of its nodes' values.
Example 1:

Input: root = [1,null,2,3]
Output: [1,3,2]
Example 2:
Input: root = []
Output: []
Example 3:
Input: root = [1]
Output: [1]
Constraints:
- The number of nodes in the tree is in the range
[0, 100]. -100 <= Node.val <= 100
Follow up: Recursive solution is trivial, could you do it iteratively?
Solution
# Definition for a binary tree node.
# class TreeNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, left=None, right=None):
# self.val = val
# self.left = left
# self.right = right
from typing import List, Optional
class Solution:
def __init__(self) -> None:
self.res = []
def dfs(self, rt: TreeNode) -> None:
if not rt:
return
self.dfs(rt.left)
self.res.append(rt.val)
self.dfs(rt.right)
def inorderTraversal(self, root: Optional[TreeNode]) -> List[int]:
self.dfs(root)
return self.res
最后更新: October 11, 2023