99.recover-binary-search-tree
Statement
Metadata
- Link: 恢复二叉搜索树
- Difficulty: Medium
- Tag:
树深度优先搜索二叉搜索树二叉树
给你二叉搜索树的根节点 root ,该树中的 恰好 两个节点的值被错误地交换。请在不改变其结构的情况下,恢复这棵树 。
示例 1:
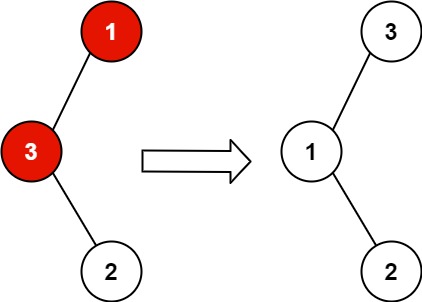
输入:root = [1,3,null,null,2]
输出:[3,1,null,null,2]
解释:3 不能是 1 的左孩子,因为 3 > 1 。交换 1 和 3 使二叉搜索树有效。
示例 2:
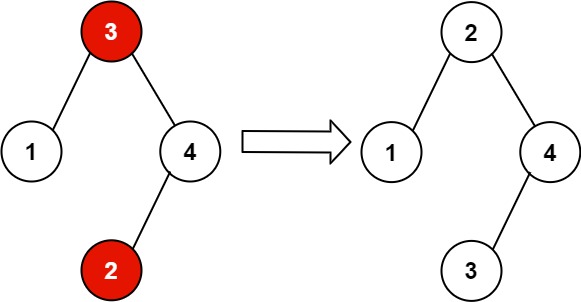
输入:root = [3,1,4,null,null,2]
输出:[2,1,4,null,null,3]
解释:2 不能在 3 的右子树中,因为 2 < 3 。交换 2 和 3 使二叉搜索树有效。
提示:
- 树上节点的数目在范围
[2, 1000]内 -231 <= Node.val <= 231 - 1
进阶:使用 O(n) 空间复杂度的解法很容易实现。你能想出一个只使用 O(1) 空间的解决方案吗?
Metadata
- Link: Recover Binary Search Tree
- Difficulty: Medium
- Tag:
TreeDepth-First SearchBinary Search TreeBinary Tree
You are given the root of a binary search tree (BST), where the values of exactly two nodes of the tree were swapped by mistake. Recover the tree without changing its structure.
Example 1:

Input: root = [1,3,null,null,2]
Output: [3,1,null,null,2]
Explanation: 3 cannot be a left child of 1 because 3 > 1. Swapping 1 and 3 makes the BST valid.
Example 2:

Input: root = [3,1,4,null,null,2]
Output: [2,1,4,null,null,3]
Explanation: 2 cannot be in the right subtree of 3 because 2 < 3. Swapping 2 and 3 makes the BST valid.
Constraints:
- The number of nodes in the tree is in the range
[2, 1000]. -231 <= Node.val <= 231 - 1
Follow up: A solution using
O(n) space is pretty straight-forward. Could you devise a constant O(1) space solution? Solution
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#include <ext/pb_ds/assoc_container.hpp>
#include <ext/pb_ds/tree_policy.hpp>
#define endl "\n"
#define fi first
#define se second
#define all(x) begin(x), end(x)
#define rall rbegin(a), rend(a)
#define bitcnt(x) (__builtin_popcountll(x))
#define complete_unique(a) a.erase(unique(begin(a), end(a)), end(a))
#define mst(x, a) memset(x, a, sizeof(x))
#define MP make_pair
using ll = long long;
using ull = unsigned long long;
using db = double;
using ld = long double;
using VLL = std::vector<ll>;
using VI = std::vector<int>;
using PII = std::pair<int, int>;
using PLL = std::pair<ll, ll>;
using namespace __gnu_pbds;
using namespace std;
template <typename T>
using ordered_set = tree<T, null_type, less<T>, rb_tree_tag, tree_order_statistics_node_update>;
template <typename T, typename S>
inline bool chmax(T &a, const S &b) {
return a < b ? a = b, 1 : 0;
}
template <typename T, typename S>
inline bool chmin(T &a, const S &b) {
return a > b ? a = b, 1 : 0;
}
#ifdef LOCAL
#include <debug.hpp>
#else
#define dbg(...)
#endif
// head
// 1 2 3 4 5 6
// 1 6 3 4 5 2
// 1 3 6 4 5 2
// 1 3 4 6 5 2
// 1 3 4 5 6 2
// 1 3 4 5 2 6
// 1 3 4 2 5 6
// 1 3 2 4 5 6
// 1 2 3 4 5 6
// 3 2 1
// 1 2 3
// 1 3 2 4
// 1 2 3 4
#ifdef LOCAL
struct TreeNode {
int val;
TreeNode *left;
TreeNode *right;
TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {}
};
#endif
class Solution {
public:
void dfs(TreeNode *root) {
if (root->left) {
dfs(root->left);
}
if (pre_) {
if (root->val < pre_->val) {
if (first_ == nullptr) {
first_ = pre_;
second_ = root;
} else {
second_ = root;
return;
}
}
}
pre_ = root;
if (root->right) {
dfs(root->right);
}
}
void recoverTree(TreeNode *root) {
pre_ = nullptr;
first_ = nullptr;
second_ = nullptr;
dfs(root);
swap(first_->val, second_->val);
}
private:
TreeNode *pre_;
TreeNode *first_;
TreeNode *second_;
};
#ifdef LOCAL
int main() {
return 0;
}
#endif
最后更新: October 11, 2023